Understanding your heart health is important for individuals living with diabetes, as the condition can increase the risk of cardiovascular problems. Angiography is a key diagnostic tool used to assess the blood vessels and heart function, helping doctors identify any blockages or issues that could impact your health. This guide will help you understand your angiography report, enabling you to make informed decisions and work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your heart health effectively.
Angiography scans are commonly used to examine blood vessels in detail and detect issues like blockages or narrowing that can lead to health problems. While reading an angiography scan is typically done by medical specialists, understanding the basics can help you feel more informed about your health and your doctor’s findings.
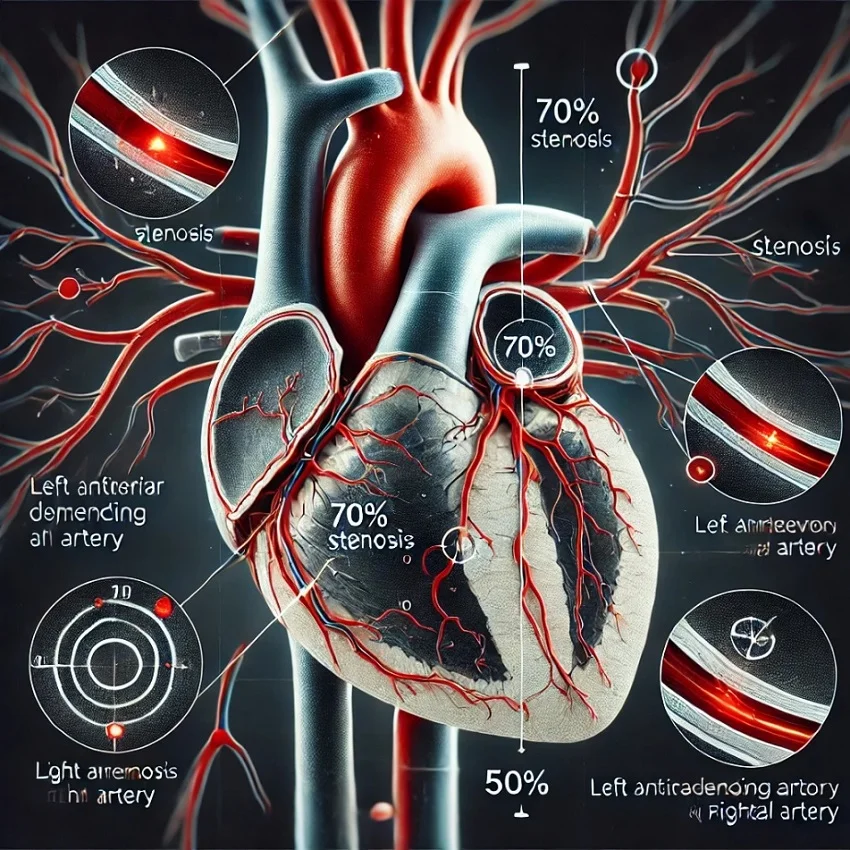
What is an Angiography Scan?
Angiography is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays, CT, or MRI combined with a special contrast dye to make blood vessels visible. It’s often used to:
- Detect blockages or narrowing (stenosis) in arteries.
- Identify aneurysms (bulges in vessel walls).
- Locate abnormalities or malformations in blood vessels.
Common types of angiography include:
- Coronary Angiography: For heart arteries.
- Cerebral Angiography: For brain blood vessels.
- Peripheral Angiography: For limbs.
What to Expect on an Angiography Scan
The scan will display images of your blood vessels filled with contrast dye, which helps highlight:
- Blood Flow: The contrast dye shows how blood moves through the vessels.
- Vessel Shape and Size: Healthy vessels appear smooth and uniform.
- Irregularities: These include blockages, narrowing, or bulges.
How Do Doctors Interpret the Scan?
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of what doctors look for in an angiography scan:
- Orientation of the Image: Doctors first determine which part of the body and which blood vessel the scan is showing. For example, coronary angiography focuses on the arteries supplying blood to the heart.
- Tracing the Blood Vessels:
- They start at the origin of the vessel (e.g., the heart’s aorta) and trace its path.
- They look for any interruptions or irregularities in blood flow.
- Checking for Narrowing or Blockages:
- Narrowing (Stenosis): Appears as a thin or pinched section of the vessel.
- Complete Blockage: The dye stops flowing, indicating an obstruction.
- Assessing Vessel Walls:
- Healthy vessel walls are smooth. Irregular walls might suggest plaque buildup or damage.
- Looking for Other Abnormalities:
- Aneurysms: Areas where the vessel bulges outward.
- Collateral Circulation: Alternate blood vessels that form to bypass blocked areas.
In an angiography report, white color typically indicates areas where the contrast dye has accumulated the most. This can point to the presence of a blockage or narrowing of blood vessels. It suggests areas where blood flow is restricted or completely blocked. This is often seen in the form of a solid white spot or area within the arteries or veins, highlighting areas of concern that may require further medical attention.
Common Findings and What They Mean
Here are some terms your doctor might use when discussing your scan:
- Normal Findings:
- Blood vessels are smooth, with no narrowing or blockages.
- Stenosis (Narrowing):
- Partial narrowing due to plaque buildup. Severe stenosis (>70%) can cause symptoms like chest pain or breathlessness.
- Occlusion (Blockage):
- A complete blockage that stops blood flow. This is often serious and requires immediate attention.
- Aneurysm:
- A bulge in the vessel wall that can weaken over time and may require monitoring or treatment.
- Collateral Circulation:
- New vessels that form to bypass blocked areas. While helpful, they often indicate an underlying issue.
What Can You Do with This Information?
While understanding your angiography scan is helpful, the detailed interpretation should always be done by a qualified doctor. Here are some tips to make the most of your results:
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor what each finding means and how it relates to your symptoms.
- Understand Severity: If there’s narrowing or blockage, ask how severe it is and what treatments are available.
- Follow Recommendations: Your doctor might suggest lifestyle changes, medications, or procedures to address the issue based on the findings.
- Be Proactive: Keep up with follow-up appointments and any additional tests recommended by your doctor.
Action Points for You
Angiography scans are powerful tools to assess blood vessel health. While they may look complex, understanding the basics such as how blood flow is visualized and what abnormalities might appear can empower you to better understand your health. Remember, always rely on your healthcare provider to interpret the results and guide your next steps. Their expertise ensures the best care for your unique situation.
If you have questions about your angiography results or what they mean, don’t hesitate to ask your doctor mainly a cardiologist. Your health is a team effort, and staying informed is an important part of this process.