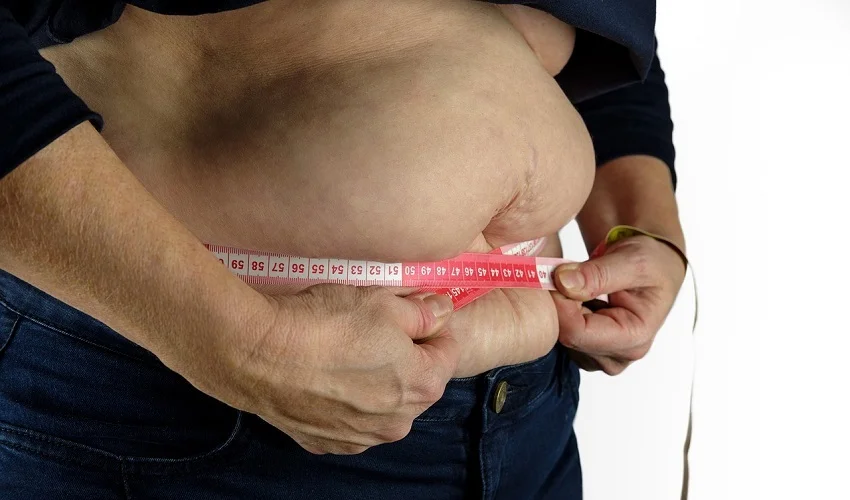
Definition of truncal obesity
Truncal obesity, also known as central obesity or abdominal obesity, refers to the excessive accumulation of fat in the abdominal area. It is characterized by a large waist circumference and an increased risk of developing various health conditions, including diabetes. Truncal obesity is often associated with an unhealthy lifestyle, such as a sedentary lifestyle and a diet high in calories and saturated fats. It is important to address truncal obesity as it can significantly impact an individual’s overall health and well-being.
Prevalence of truncal obesity
Truncal obesity refers to the accumulation of excess fat around the waist and abdomen. It is a common condition that has been linked to various health problems, including diabetes. The prevalence of truncal obesity has been on the rise in recent years, with a significant number of individuals being affected by this condition. Studies have shown that there is a strong association between truncal obesity and the development of diabetes, with obese individuals being at a higher risk of developing the disease. Understanding the prevalence of truncal obesity is crucial in addressing the growing burden of diabetes and implementing effective prevention and management strategies.
Link between truncal obesity and diabetes
Research has shown a strong link between truncal obesity and the development of diabetes. The excess fat in the abdominal area leads to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. This can result in high blood sugar levels and eventually lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. It is important to address truncal obesity through lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and a healthy diet to reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Causes of Truncal Obesity
Genetic factors
Truncal obesity, or excess fat accumulation around the waist area, has been found to have a strong association with diabetes. Genetic factors play a significant role in this link, as certain genes can predispose individuals to both truncal obesity and diabetes. Studies have identified specific gene variants that are associated with an increased risk of developing both conditions. Understanding these genetic factors can help in the development of targeted interventions and personalized treatment strategies for individuals at risk of developing diabetes due to truncal obesity.
Sedentary lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by a lack of physical activity, has been identified as a significant risk factor for the development of diabetes. Studies have shown that individuals who engage in prolonged periods of sitting or inactivity have a higher likelihood of developing insulin resistance, which can lead to the onset of type 2 diabetes. Sedentary behavior not only contributes to weight gain and obesity, but it also negatively impacts glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Therefore, it is crucial to promote regular physical activity and reduce sedentary time to prevent and manage diabetes.
Unhealthy diet
An unhealthy diet is one of the main diabetes risk factors contributing to the link between truncal obesity and diabetes. Consuming high amounts of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can lead to weight gain and the accumulation of fat around the waistline. This excess fat, known as truncal obesity, is strongly associated with insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes. Additionally, an unhealthy diet can also lead to other risk factors for diabetes, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels. Therefore, adopting a healthy and balanced diet is crucial in preventing and managing truncal obesity and diabetes.
Effects of Truncal Obesity on Diabetes
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a key factor in the link between truncal obesity and diabetes. When a person has excess fat around their abdomen, it can lead to a decrease in the body’s sensitivity to insulin. This means that the body needs to produce more insulin in order to keep blood sugar levels in check. Over time, the pancreas may become overworked and unable to produce enough insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels and the development of diabetes. Therefore, addressing insulin resistance through lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, is crucial in preventing and managing diabetes in individuals with truncal obesity.
Inflammation
Truncal obesity has also been strongly linked to the development of chronic inflammation. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can contribute to the development of various health conditions, including diabetes. Studies have shown that adipose tissue, particularly the visceral fat found around the abdomen, secretes pro-inflammatory substances called cytokines. These cytokines can disrupt the normal functioning of insulin and promote insulin resistance, a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. Therefore, reducing truncal obesity and addressing chronic inflammation are important strategies in the prevention and management of diabetes.
Dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia refers to an abnormal level of lipids or fats in the blood. It is a common condition associated with obesity and is often seen in individuals with truncal obesity. Truncal obesity, also known as central obesity, is the accumulation of fat around the waist and abdomen. The excess fat in the abdominal area can lead to an increase in triglyceride levels and a decrease in HDL cholesterol levels, which are both risk factors for diabetes. Therefore, the link between truncal obesity and dyslipidemia plays a significant role in the development of diabetes.
Prevention and Management of Truncal Obesity
Regular physical activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of developing diabetes. Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming can help burn calories and improve insulin sensitivity. Additionally, regular exercise can help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and enhance overall cardiovascular health. It is recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days. Incorporating regular physical activity into our daily routine can significantly contribute to the prevention and management of diabetes.
Balanced diet
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing truncal obesity and preventing diabetes. It involves consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods in appropriate portions. A balanced diet should include a mix of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. By following a balanced diet, individuals can maintain a healthy weight, reduce the accumulation of fat around the waistline, and improve insulin sensitivity. Additionally, a balanced diet provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and well-being. It is important to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized balanced diet plan that suits individual needs and goals.
Behavioral changes
Truncal obesity refers to the accumulation of excess fat around the waist and abdomen and it has been strongly linked to the development of diabetes. Behavioral changes play a crucial role in managing truncal obesity and reducing the risk of diabetes. Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle are important behavioural changes that can help prevent and manage truncal obesity. These changes not only promote weight loss but also improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. By making these behavioural changes, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the burden of diabetes.
Importance of addressing truncal obesity
Truncal obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of diabetes. Excess fat stored in the abdominal area can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can result in elevated blood sugar levels and eventually lead to the onset of diabetes. Therefore, it is crucial to address truncal obesity through lifestyle modifications such as regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and weight management. By targeting this specific type of obesity, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and improve their overall health.
Potential for reducing diabetes risk
Excess fat around the waist and abdomen can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. This can result in high blood sugar levels and eventually lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. However, there is potential for reducing the risk of diabetes through lifestyle changes. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and weight management can help decrease truncal obesity and improve insulin sensitivity. By adopting healthy habits, individuals can lower their chances of developing diabetes and improve their overall health.
Need for further research
Truncal obesity has been consistently linked to an increased risk of developing diabetes. However, there is still a need for further research to fully understand the underlying mechanisms and potential interventions. By investigating the specific pathways through which truncal obesity contributes to diabetes, researchers can develop targeted strategies for prevention and treatment. Additionally, exploring the impact of lifestyle factors, such as diet and physical activity, on the relationship between truncal obesity and diabetes can provide valuable insights. Further research in this area is crucial for improving our understanding of the link between truncal obesity and diabetes and developing effective strategies to mitigate its impact on public health.