Sleep is an essential aspect of our daily lives, but its significance often goes unnoticed, particularly among individuals with diabetes. Proper blood sugar control is paramount for managing diabetes effectively. While diet and physical activity are widely acknowledged as key contributors, sleep deprivation can have a substantial impact on blood sugar levels. In this article, we will delve into the relationship between sleep deprivation and blood sugar control, uncover the underlying mechanisms, and present strategies for promoting healthy sleep habits among individuals with diabetes.
The Link between Sleep and Blood Sugar Control
Importance of Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range is vital for individuals with diabetes. Consistently high blood sugar, known as hyperglycemia, can lead to various complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems. Conversely, low blood sugar, known as hypoglycemia, can cause dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. By understanding the connection between sleep and blood sugar control, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively.
Recognizing the Role of Sleep
Sleep is a fundamental process that allows our bodies to rest, rejuvenate, and repair. It is during sleep that essential bodily functions, including hormone regulation and cellular regeneration, take place. However, sleep is more than just a state of rest. It also influences various physiological processes, including blood sugar regulation. Understanding the impact of sleep deprivation on blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes to maintain optimal control of their condition.
Sleep Deprivation and Insulin Resistance
Insulin and Its Role in Blood Sugar Regulation
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a central role in regulating blood sugar levels. When we consume carbohydrates, the body breaks them down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. Insulin helps transport glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, where it is used for energy or stored for later use. In individuals with diabetes, insulin either cannot be produced (Type 1 diabetes) or is not utilized effectively (Type 2 diabetes).
How Sleep Deprivation Impacts Insulin Sensitivity
Sleep deprivation has been shown to contribute to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. Studies have indicated that even a single night of inadequate sleep can lead to decreased insulin sensitivity. This means that the body requires higher levels of insulin to transport glucose from the bloodstream into the cells effectively. The resulting insulin resistance can disrupt blood sugar control and contribute to the development or progression of diabetes.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Insulin Resistance
Chronic sleep deprivation can significantly contribute to insulin resistance and impair blood sugar regulation. Research has shown that individuals who consistently get less sleep than recommended are at a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, existing diabetes management can be hindered by poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep duration. By recognizing the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation on insulin sensitivity, individuals with diabetes can prioritize healthy sleep habits as part of their overall treatment plan.
Sleep Deprivation and Glucose Metabolism
Glucose Homeostasis: An Overview
Glucose homeostasis refers to the body’s ability to maintain stable blood sugar levels. This delicate balance is achieved through a complex interplay of various hormones, enzymes, and signaling pathways. Disruptions in this intricate system can lead to abnormal blood sugar levels and, consequently, diabetes.
The Role of Sleep in Glucose Metabolism
During sleep, the body undergoes crucial metabolic processes, including the regulation of glucose metabolism. Studies have shown that sleep deprivation can impair glucose tolerance, increasing the risk of elevated blood sugar levels. Sleep restriction can result in reduced glucose uptake by the muscles and liver, leading to higher blood sugar concentrations.
Impaired Glucose Tolerance due to Sleep Deprivation
Impaired glucose tolerance is characterized by the body’s inability to effectively handle a glucose load, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Sleep deprivation has been found to disrupt glucose tolerance, making individuals more susceptible to abnormal blood sugar levels. Chronic sleep deprivation can contribute to persistent impaired glucose tolerance, potentially leading to the development of Type 2 diabetes.
Sleep Deprivation and Hormonal Imbalance
The Role of Hormones in Blood Sugar Regulation
Hormones play a crucial role in maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, lowers blood sugar by facilitating glucose uptake by cells. Conversely, hormones such as cortisol, ghrelin, and leptin influence blood sugar levels through various mechanisms.
Sleep Deprivation and Cortisol Levels
Cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone,” is involved in regulating blood sugar levels, metabolism, and immune function. Sleep deprivation has been shown to elevate cortisol levels, disrupting the delicate balance required for optimal blood sugar control. Elevated cortisol levels can increase blood sugar concentrations and contribute to insulin resistance.
Influence of Sleep Deprivation on Ghrelin and Leptin
Ghrelin and leptin are hormones that regulate appetite and energy balance. Ghrelin stimulates hunger, while leptin signals satiety. Sleep deprivation can disrupt the balance of these hormones, leading to increased appetite and a higher likelihood of overeating or consuming unhealthy foods. This can further disrupt blood sugar control and contribute to weight gain, a common risk factor for Type 2 diabetes.
Sleep Deprivation and Appetite Regulation
Appetite Regulation Mechanisms
Appetite regulation involves complex interactions between hormones, the brain, and sensory cues. Adequate sleep plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of these mechanisms. Disruptions in sleep can lead to dysregulation of appetite signals, increasing the risk of overeating and poor food choices.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Appetite Hormones
Sleep deprivation has been linked to alterations in appetite-regulating hormones, namely ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin levels increase, promoting hunger and cravings, while leptin levels decrease, reducing feelings of fullness and satiety. The resulting imbalance can lead to overconsumption of calories and a higher likelihood of blood sugar dysregulation.
Increased Hunger and Cravings due to Sleep Loss
Research has shown that individuals who experience sleep deprivation tend to have increased hunger, particularly for high-calorie and carbohydrate-rich foods. These food choices can further exacerbate blood sugar control issues, making it challenging for individuals with diabetes to maintain optimal glucose levels. Utilizing tools like a Weight Loss Calculator can help track caloric intake and support healthier weight management, which in turn may improve blood sugar regulation. Recognizing the impact of sleep loss on appetite regulation is crucial for individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions regarding their dietary choices.
Strategies to Promote Healthy Sleep Habits
Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule is vital for promoting healthy sleep habits. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate the body’s internal clock, promoting better sleep quality and duration. Individuals with diabetes should prioritize consistency in their sleep patterns to support blood sugar control.
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Creating a sleep-friendly environment can significantly impact the quality of sleep. A comfortable and dark bedroom, free from distractions and noise, can enhance the ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. Additionally, ensuring an appropriate temperature and ventilation can contribute to a restful night’s sleep.
Practicing Relaxation Techniques
Engaging in relaxation techniques before bedtime can help calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep. Activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and gentle stretching can promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. Avoiding stimulating activities, such as vigorous exercise or intense screen time, close to bedtime is also recommended.
Limiting Stimulants and Electronics before Bedtime
Caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can disrupt sleep patterns and should be avoided close to bedtime. These substances can interfere with falling asleep and negatively impact sleep quality. Additionally, the blue light emitted by electronic devices can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep. Limiting the use of electronic devices, such as smartphones and tablets, in the evening hours can contribute to better sleep hygiene.
The Importance of Sleep for Diabetes Management
Blood Sugar Monitoring and Sleep
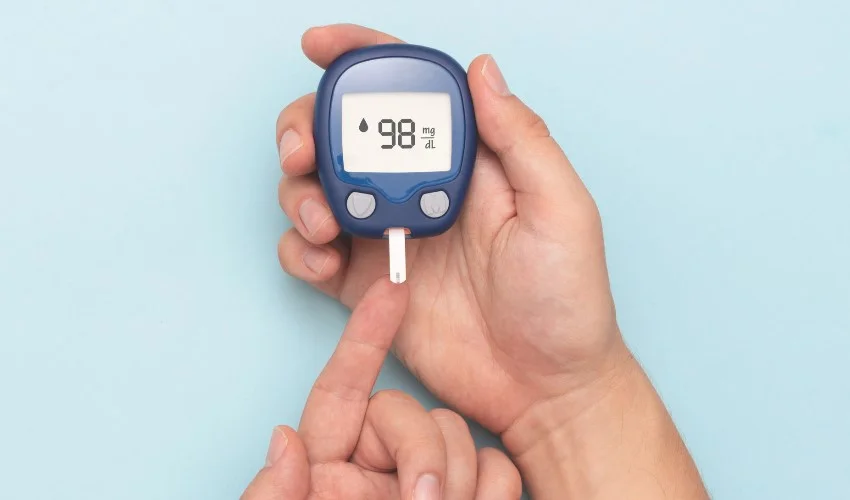
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for individuals with diabetes to track their levels and make informed decisions regarding their treatment. You can also assess your risk for diabetes using a Diabetes Risk Calculator, which can provide valuable insights into your overall health. Monitoring blood sugar before bedtime and upon waking can provide valuable insights into the impact of sleep on glucose control. By identifying patterns and trends, individuals can adjust their diabetes management strategies accordingly.
Sleep Quality and Medication Efficacy
The effectiveness of diabetes medications can be influenced by sleep quality. Poor sleep can impact medication absorption, metabolism, and overall efficacy. Individuals should discuss their sleep patterns and concerns with their healthcare professionals to ensure optimal medication management.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Individuals with diabetes should collaborate closely with their healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans that address the multifaceted aspects of their condition, including sleep deprivation. Healthcare professionals can provide guidance, support, and evidence-based strategies to improve sleep quality and blood sugar control.
Sleep deprivation can significantly impact blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes. From insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance to hormonal imbalances and disrupted appetite regulation, sleep loss poses significant challenges for managing diabetes effectively. By understanding the connection between sleep and blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can prioritize healthy sleep habits as part of their comprehensive diabetes management plan. Strategies such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a sleep-friendly environment, practicing relaxation techniques, and limiting stimulants before bedtime can contribute to better sleep quality and improved blood sugar control. It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to collaborate with healthcare professionals and remain proactive in addressing sleep deprivation to optimize their overall health and well-being.