Definition of glycemic index
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after it is consumed. It ranks carbohydrates on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how much they increase blood sugar levels compared to pure glucose. Foods with a high glycemic index (GI) are quickly digested and absorbed, causing a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, foods with a low GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Understanding the glycemic index can be helpful for managing blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with diabetes or those looking to maintain stable energy levels throughout the day.
Importance of glycemic index
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Understanding the glycemic index is important because it can help individuals make informed choices about their diet and manage their blood sugar levels. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar, leading to a surge of insulin and potentially contributing to health issues such as weight gain, diabetes, and heart disease. On the other hand, foods with a low glycemic index release sugar into the bloodstream gradually, providing a more sustained source of energy and promoting better overall health. By considering the glycemic index of foods, individuals can make healthier choices that support stable blood sugar levels and long-term well-being.
Factors affecting glycemic index
The glycemic index of a food is influenced by several factors. One of the main factors is the type of carbohydrate present in the food. Foods that contain simple carbohydrates, such as white bread and sugary drinks, tend to have a higher glycemic index. On the other hand, foods that contain complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and legumes, have a lower glycemic index. Another factor that affects the glycemic index is the cooking method used. Foods that are cooked for a longer duration, such as boiled potatoes, have a higher glycemic index compared to foods that are cooked for a shorter duration, such as steamed vegetables. Additionally, the presence of fiber and fat in a food can also impact its glycemic index. Foods that are high in fiber and fat, such as fruits and nuts, tend to have a lower glycemic index. Overall, understanding the factors that affect the glycemic index can help individuals make informed choices about their dietary intake and manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
What is Dosa?
Introduction to dosa
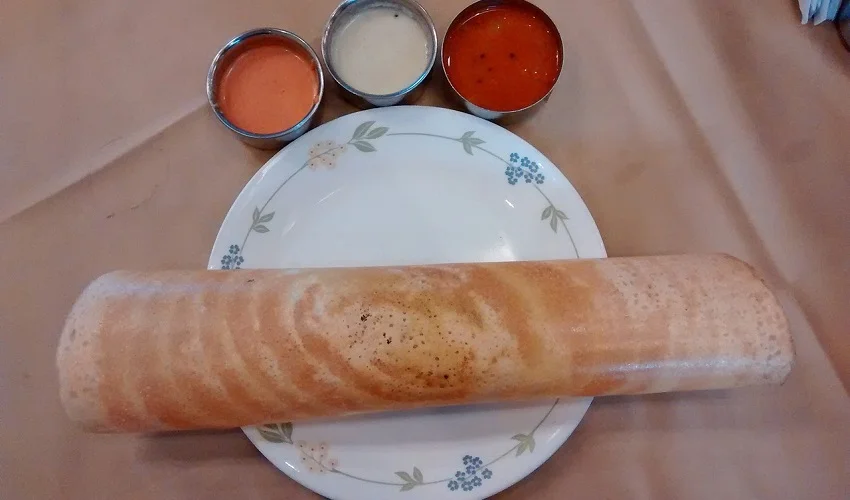
Dosa, a popular South Indian dish, is a thin and crispy pancake made from fermented rice and lentil batter. It is a staple breakfast item in many households and is loved for its delicious taste and versatility. The glycemic index of dosa refers to how quickly it raises blood sugar levels after consumption. Understanding the glycemic index of dosa is important for individuals with diabetes or those who are following a low-glycemic diet. In this article, we will explore the concept of glycemic index in relation to dosa and its impact on overall health and well-being.
Ingredients used in dosa
Dosa is a popular South Indian dish that is enjoyed by people of all ages. It is made using a fermented batter of rice and lentils, which gives it a unique and delicious taste. The main ingredients used in dosa include rice, urad dal (split black gram), fenugreek seeds, and salt. These ingredients are soaked, ground, and then left to ferment overnight, resulting in a light and crispy dosa. Other optional ingredients such as cumin seeds, curry leaves, and ginger can also be added to enhance the flavor. The combination of these ingredients creates a perfect balance of flavors and textures, making dosa a wholesome and satisfying meal.
Different types of dosa
Dosa, a popular South Indian dish, comes in various types, each with its own unique taste and preparation method. From the classic plain dosa to the flavorful masala dosa, there is a dosa for every palate. Other popular variations include rava dosa, which is made with semolina, and onion dosa, which is filled with a delicious onion filling. Each type of dosa offers a different culinary experience, making it a versatile and beloved dish in Indian cuisine.
Understanding Glycemic Index
Definition of glycemic index
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after consumption. It is a scale from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating a faster rise in blood sugar. A low glycemic index (GI) indicates that a food has a slower and more gradual effect on blood sugar levels, while a high GI means that the food causes a rapid spike in blood sugar. Understanding the glycemic index can be helpful for individuals managing diabetes or those looking to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
How glycemic index is measured
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. It is determined by comparing the blood sugar response to a specific amount of a food with the response to the same amount of glucose or white bread. The GI scale ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating a faster and larger increase in blood sugar. To measure the GI of a food, participants are typically given a fixed amount of the food and their blood sugar levels are monitored over a period of time. The average blood sugar response is then compared to the response to glucose or white bread to calculate the GI value.
Interpreting glycemic index values
The glycemic index (GI) is a measurement of how quickly a particular food raises blood sugar levels. It is a scale that ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating a faster rise in blood sugar. When interpreting glycemic index values, it is important to consider that individual responses to different foods can vary. Factors such as cooking methods, food combinations, and individual metabolism can influence how a food affects blood sugar levels. Therefore, it is recommended to use the glycemic index as a guide rather than a definitive measure of a food’s impact on blood sugar levels.
Glycemic Index of Dosa
Glycemic index of different types of dosa
The glycemic index of different types of dosa can vary significantly. The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. In general, dosa made from refined grains, such as white rice, tends to have a higher glycemic index compared to dosa made from whole grains like brown rice or millets. Additionally, the cooking method and ingredients used can also impact the glycemic index of dosa. For example, dosa made with fermented batter may have a lower glycemic index compared to dosa made with non-fermented batter. It is important to consider the glycemic index of dosa, especially for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels.
Factors affecting the glycemic index of dosa
The glycemic index of dosa, a popular South Indian dish, is influenced by several factors. One of the main factors is the type of rice used in the batter. Different varieties of rice have different starch compositions, which can affect the rate at which the carbohydrates in dosa are digested and absorbed into the bloodstream. Additionally, the fermentation process used in preparing the dosa batter can also impact its glycemic index. Fermentation breaks down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars, resulting in a lower glycemic index. Other factors such as cooking time, thickness of the dosa, and the presence of fats or proteins in the dish can also influence its glycemic index. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed choices about their dietary intake and manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Comparison of dosa glycemic index with other foods
The dosa glycemic index is a measure of how quickly the carbohydrates in dosa are digested and absorbed into the bloodstream, resulting in a rise in blood sugar levels. When compared to other foods, dosa generally has a lower glycemic index, making it a better choice for individuals looking to manage their blood sugar levels. This is because dosa is made from fermented rice and lentil batter, which slows down the digestion process and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. In contrast, foods with a higher glycemic index, such as white bread or sugary snacks, are quickly digested and can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar. Therefore, incorporating dosa into your diet can be a beneficial way to enjoy a delicious meal while keeping your blood sugar in check.
Health Implications
Impact of high glycemic index on blood sugar levels
The impact of high glycemic index on blood sugar levels is significant. Foods with a high glycemic index, such as dosa, can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This is because these foods are quickly broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. When blood sugar levels rise too quickly, it can lead to a spike in insulin production and potentially contribute to the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Therefore, individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes should be mindful of their glycemic index intake and opt for foods with a lower glycemic index to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Benefits of consuming low glycemic index foods
Consuming low glycemic index foods, such as dosa, can have several benefits for our health. These foods are digested and absorbed more slowly, which helps in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. This is especially beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those trying to manage their weight. Additionally, low glycemic index foods provide a steady release of energy, keeping us fuller for longer and reducing the chances of overeating. Incorporating dosa, with its low glycemic index, into our diet can contribute to better blood sugar control, weight management, and overall health.
Role of dosa in a balanced diet
Dosa, a popular South Indian dish, plays a significant role in a balanced diet. It is not only delicious but also nutritious, making it a versatile choice for people of all ages. Dosa is made from fermented rice and lentil batter, which provides a good amount of carbohydrates, proteins, and essential minerals. This combination makes dosa a great source of energy and helps in maintaining a healthy metabolism. Additionally, dosa is low in fat and cholesterol, making it a heart-healthy option. Including dosa in a balanced diet can contribute to weight management, as it is relatively low in calories. Moreover, dosa is often served with a variety of chutneys and sambar, which are rich in vitamins and antioxidants, further enhancing its nutritional value. Overall, incorporating dosa into a balanced diet can provide a delicious and wholesome meal that is beneficial for overall health and well-being.
Summary of key points
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Dosa, a popular South Indian dish, has a relatively low glycemic index compared to other carbohydrate-rich foods. This means that dosa is digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. The low glycemic index of dosa makes it a suitable food choice for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels. Additionally, dosa is a good source of carbohydrates, proteins, and essential nutrients, making it a nutritious and filling meal option.
Importance of considering glycemic index in food choices
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. It is important to consider the glycemic index in food choices because it can impact our overall health and well-being. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, leading to increased hunger, cravings, and potential weight gain. On the other hand, foods with a low glycemic index provide a slower release of sugar into the bloodstream, promoting sustained energy levels and better blood sugar control. By choosing foods with a lower glycemic index, we can maintain stable blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease, and support overall health and weight management.
Final thoughts on dosa glycemic index
In conclusion, understanding the glycemic index of dosa can be beneficial for individuals looking to manage their blood sugar levels. While dosa is generally considered to have a high glycemic index, there are ways to make it more suitable for those with diabetes or insulin resistance. Opting for fermented dosa made from whole grains, such as brown rice or millets, can help lower the glycemic index. Additionally, pairing dosa with protein-rich foods, like lentils or yogurt, can further slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice on incorporating dosa into a balanced and healthy diet.