What is glycemic index?
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after it is consumed. It ranks carbohydrates on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how quickly they are digested and absorbed into the bloodstream. Foods with a high glycemic index (GI) are quickly digested and cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, while foods with a low GI are digested more slowly and result in a slower rise in blood sugar. Understanding the glycemic index can be particularly important for diabetics, as it can help them make informed choices about the foods they eat to manage their blood sugar levels.
Importance of glycemic index for diabetics
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a particular food raises blood sugar levels. For diabetics, understanding the glycemic index is important as it helps in managing blood sugar levels effectively. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, which can be problematic for diabetics. On the other hand, foods with a low glycemic index are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. By choosing foods with a low glycemic index, diabetics can better control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
How does glycemic index affect blood sugar levels?
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after consumption. For individuals with diabetes, understanding the glycemic index is crucial as it helps in managing blood sugar levels. Foods with a high glycemic index are quickly digested and absorbed, causing a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, foods with a low glycemic index are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual and steady increase in blood sugar levels. By choosing foods with a low glycemic index, individuals with diabetes can better control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Understanding Paneer
What is paneer?
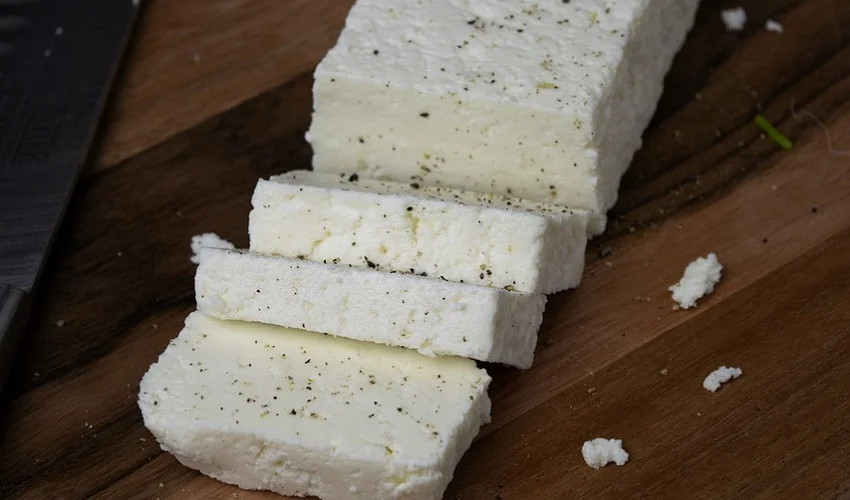
Paneer is a type of fresh cheese that is commonly used in Indian cuisine. It is made by curdling milk with lemon juice or vinegar, resulting in a soft and crumbly texture. Paneer is a rich source of protein and calcium, making it a popular choice for vegetarians and those looking to increase their protein intake. It is also low in carbohydrates and has a low glycemic index, which means it does not cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This makes paneer a suitable option for individuals with diabetes, as it can help regulate blood sugar levels. Additionally, paneer is versatile and can be used in a variety of dishes such as curries, stir-fries, and desserts.
Nutritional composition of paneer
Paneer is a popular Indian cheese that is widely consumed and enjoyed by people of all ages. It is known for its rich and creamy texture, as well as its versatility in various dishes. When it comes to the nutritional composition of paneer, it is a good source of protein, calcium, and phosphorus. Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair, while calcium and phosphorus are important for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Additionally, paneer is low in carbohydrates, making it a suitable option for individuals with diabetes who need to manage their blood sugar levels. Overall, paneer is a nutritious and delicious addition to a balanced diet.
Benefits of paneer for diabetics
Paneer, also known as cottage cheese, is a popular dairy product that offers several benefits for diabetics. One of the main benefits of paneer is its low glycemic index, which means it does not cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This makes it a suitable choice for individuals with diabetes who need to manage their blood sugar levels. Additionally, paneer is a good source of protein, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote satiety. It also contains essential nutrients like calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D, which are important for maintaining bone health. Incorporating paneer into a balanced diet can be a nutritious and delicious way for diabetics to enjoy their meals while managing their condition.
Glycemic Index of Paneer
What is glycemic index of paneer?
The glycemic index (GI) of paneer refers to how quickly the carbohydrates in paneer are digested and absorbed into the bloodstream, causing a rise in blood sugar levels. Paneer has a very low glycemic index, which means it has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. This makes it a suitable food for diabetics as it helps in managing blood sugar levels. The low GI of paneer is attributed to its high protein and fat content, which slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Additionally, paneer is also rich in essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus, making it a healthy choice for individuals with diabetes.
Factors affecting glycemic index of paneer
Paneer is a popular dairy product that is often included in the diet of individuals with diabetes due to its low glycemic index. However, the glycemic index of paneer can vary depending on several factors. One of the main factors is the type of milk used to make the paneer. Paneer made from full-fat milk may have a higher glycemic index compared to paneer made from skimmed or low-fat milk. Another factor is the method of preparation. Paneer that is made by curdling milk with lemon juice or vinegar may have a lower glycemic index compared to paneer made with commercial curdling agents. Additionally, the age of the paneer can also affect its glycemic index. Fresh paneer may have a lower glycemic index compared to aged paneer. Therefore, individuals with diabetes should consider these factors when consuming paneer to better manage their blood sugar levels.
Comparison of paneer’s glycemic index with other foods
Paneer, a popular Indian cheese made from milk, has a low glycemic index, making it a suitable choice for individuals with diabetes. When compared to other foods, paneer has a lower glycemic index than most carbohydrates, including white bread, rice, and potatoes. This means that consuming paneer does not cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, making it a healthier option for diabetics. Additionally, paneer is rich in protein and calcium, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote overall health. Therefore, incorporating paneer into a balanced diet can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
Effects of Paneer on Blood Sugar Levels
How does paneer affect blood sugar levels?
Paneer, a popular Indian cheese made from milk, is a low glycemic index food that can be beneficial for diabetics. It is a rich source of protein and contains very little carbohydrates, which means it has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Paneer is also high in calcium, which is important for maintaining bone health. Additionally, the protein in paneer helps to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, further preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. However, it is still important for diabetics to consume paneer in moderation and as part of a balanced diet, as excessive intake can lead to weight gain and other health issues.
Paneer as a low glycemic index food
Paneer is a popular Indian cheese that is not only delicious but also has a low glycemic index. This makes it an excellent food choice for individuals with diabetes. The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index are digested and absorbed slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Paneer is made from milk, which contains lactose, a type of sugar. However, the process of making paneer involves curdling the milk and removing the whey, resulting in a cheese that is low in lactose. This means that paneer has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels, making it a suitable option for diabetics. Additionally, paneer is a good source of protein and calcium, which are important nutrients for maintaining overall health. Incorporating paneer into a balanced diet can help diabetics manage their blood sugar levels while enjoying a tasty and nutritious food choice.
Benefits of paneer in managing diabetes
Paneer, a type of Indian cheese, is not only delicious but also offers several benefits for managing diabetes. Firstly, paneer is a low glycemic index food, which means it causes a slow and steady rise in blood sugar levels. This is particularly beneficial for diabetics as it helps to prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar. Additionally, paneer is a good source of protein, which helps to keep you feeling full and satisfied for longer periods of time. This can be especially helpful for diabetics who need to manage their weight and control their appetite. Lastly, paneer is rich in calcium, which is important for maintaining strong bones and teeth. This is particularly important for diabetics who may be at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis. Overall, incorporating paneer into a diabetes-friendly diet can provide numerous benefits for managing blood sugar levels and overall health.
Incorporating Paneer in a Diabetic Diet
How to include paneer in a diabetic diet?
Including paneer in a diabetic diet can be a healthy and delicious choice. Paneer, also known as cottage cheese, is a low glycemic index food, which means it does not cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels. This makes it an ideal option for individuals with diabetes who need to manage their blood sugar levels. Paneer is rich in protein, which helps in keeping you feeling full and satisfied for longer periods, reducing the temptation to snack on unhealthy foods. Additionally, paneer is a good source of calcium and other essential nutrients, making it beneficial for overall health. To include paneer in a diabetic diet, it can be added to salads, stir-fries, curries, or consumed as a snack. However, it is important to consume paneer in moderation and consider portion sizes to maintain a balanced diet. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on incorporating paneer into a diabetic meal plan.
Recommended portion size of paneer
Paneer is a popular dairy product that is often consumed by individuals with diabetes. When it comes to managing blood sugar levels, portion control is key. The recommended portion size of paneer for diabetics is about 30 grams, which is roughly equivalent to one small slice. This moderate serving size helps to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels while still allowing individuals to enjoy the nutritional benefits of paneer. It is important for diabetics to consult with their healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate portion size of paneer based on their individual needs and dietary goals.
Recipes and meal ideas with paneer for diabetics
Paneer is a versatile ingredient that can be included in various recipes and meal ideas for diabetics. Its low glycemic index makes it a suitable choice for managing blood sugar levels. Some delicious options include paneer tikka, paneer curry, and paneer stir-fry with vegetables. These dishes not only provide a good source of protein but also add a creamy and satisfying texture to meals. Additionally, paneer is rich in calcium and can help support bone health. It is important to note that portion control is key when including paneer in a diabetic meal plan, as it is high in fat. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help determine the appropriate amount of paneer to include in a balanced diet for diabetics.
Summary of the importance of glycemic index for diabetics
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. For diabetics, understanding the glycemic index is crucial as it helps in managing blood sugar levels effectively. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, leading to spikes and crashes in energy levels. On the other hand, foods with a low glycemic index are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual and steady rise in blood sugar. By incorporating low glycemic index foods into their diet, diabetics can maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. Therefore, it is important for diabetics to be aware of the glycemic index and make informed food choices to better manage their condition.
Benefits of including paneer in a diabetic diet
Including paneer in a diabetic diet can offer several benefits. Firstly, paneer is a low glycemic index (GI) food, which means it does not cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. This makes it a suitable choice for individuals with diabetes who need to manage their blood sugar levels. Additionally, paneer is a good source of protein, which can help promote satiety and control hunger cravings. It also contains essential nutrients like calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D, which are important for maintaining bone health. Moreover, paneer is a versatile ingredient that can be incorporated into various dishes, making it easier to follow a balanced and enjoyable diabetic diet. Overall, including paneer in a diabetic diet can contribute to better blood sugar control, improved satiety, and enhanced nutrient intake.
Final thoughts on paneer and diabetes management
In conclusion, paneer can be a beneficial addition to a diabetes management plan. With its low glycemic index, it has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels, making it a suitable choice for diabetics. Additionally, paneer is a good source of protein and calcium, which are essential for overall health. However, it is important to consume paneer in moderation and as part of a balanced diet. As with any food, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making any significant changes to your diet.