The pancreas is a remarkable organ that has a profound impact on our body’s ability to maintain stable blood sugar levels and digest food efficiently. As discussed in the earlier article, it plays both endocrine and exocrine roles. But what happens when this essential organ starts underperforming, especially in its ability to produce insulin? In this article, we delve into methods that can stimulate the pancreas to not only produce more insulin but also potentially revive its beta cells.
Role of Pancreas in our Body:
The pancreas is a vital organ responsible for producing about 8 ounces of digestive juices daily, aiding in the breakdown of food for energy. These juices are a combination of enzymes, including lipase, which collaborates with the liver-produced bile to digest fats; protease, which not only decomposes proteins but also offers protection against certain bacteria and yeasts in the intestines; and amylase, responsible for breaking down starches into sugars to fuel the body. Beyond these digestive enzymes, the pancreas plays a pivotal role in hormone production that regulates various body functions. Insulin, primarily produced by the beta cells which constitute approximately 75% of the pancreas’s hormone-producing cells, facilitates the utilization of sugar for energy. Conversely, when blood sugar levels dip, the alpha cells, comprising around 20% of the hormone-producing cells, release glucagon, signaling the liver to introduce additional sugar into the bloodstream. While gastrin, a hormone prompting the secretion of stomach acids, is mainly produced in the stomach, a minor fraction is attributed to the pancreas. Furthermore, the pancreas’s beta cells also generate amylin, a hormone instrumental in appetite regulation and the timing of stomach content release.
Understanding the Importance of Insulin
Insulin, produced by the pancreas’s beta cells, is pivotal in ensuring that our body uses sugar effectively. When you consume food, sugar levels in your blood rise. It is insulin’s responsibility to facilitate the absorption of this sugar by cells, providing them energy and restoring sugar levels in the blood to their optimal state.
However, complications arise when there is inadequate insulin production, as seen in conditions like type 1 and type 2 diabetes. So, how can one stimulate the pancreas to enhance insulin production and possibly rejuvenate pancreatic cells?
Linking between Pancreas and Diabetes Type-2
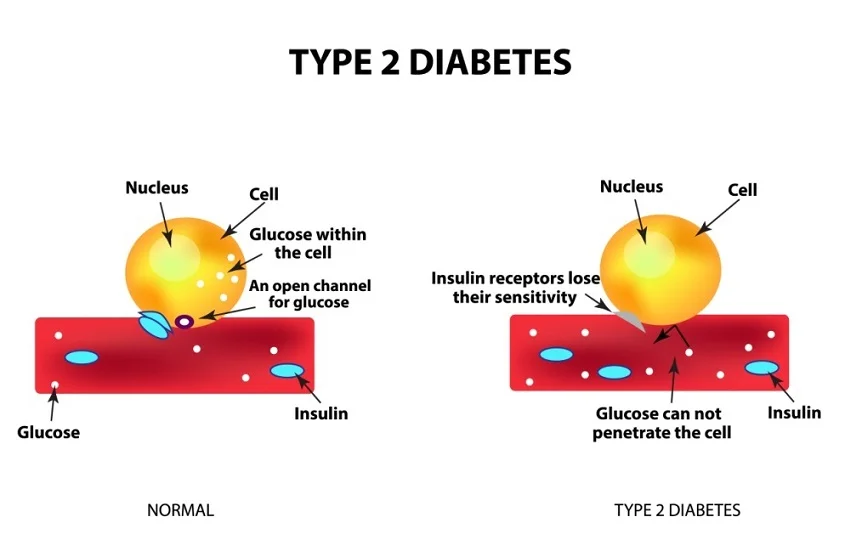
The pancreas, nestled deep within the abdomen behind the stomach, plays a pivotal role in our digestive system and overall health. This vital organ not only produces enzymes aiding in food digestion but also secretes hormones crucial for regulating body functions. One such hormone is insulin, which serves as a gatekeeper to our cells, allowing glucose, the sugar our body uses for energy, to enter and fuel them.
However, complications arise when the pancreas either does not produce sufficient insulin or the body fails to use it efficiently. The result? An accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream, a condition known as hyperglycemia. This excessive glucose level manifests in symptoms like increased thirst, nausea, and difficulty breathing. If left unchecked, hyperglycemia can escalate to life-threatening situations.
At the heart of Type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance, wherein the body’s cells become less receptive to insulin’s actions, leading to erratic blood glucose levels. In some cases, while the pancreas continues to produce insulin, it might not be in adequate amounts. Often, Type 2 diabetes is a product of both deficient insulin production and its inefficient utilization. Several factors contribute to the onset of this condition, including genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, poor dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles, and obesity.
Managing Type 2 diabetes involves a multi-faceted approach. Dietary and lifestyle modifications form the cornerstone of treatment. Additionally, medications can be instrumental in stabilizing glucose levels. Some drugs focus on reducing the glucose concentration in the blood, while others boost insulin production or enhance the body’s sensitivity to it. By understanding the intricate relationship between the pancreas and Type 2 diabetes, one can better navigate the condition and adopt strategies for a healthier life.
Strategies to Stimulate the Pancreas
Dietary Changes:
-
- Low-Carb Diet: A diet low in carbohydrates can reduce the demand on the pancreas to produce insulin.
- Include Anti-inflammatory Foods: Foods such as turmeric, berries, and fatty fish can reduce inflammation and potentially support pancreatic health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking sufficient water can aid in maintaining the health of all cells, including pancreatic cells.
Regular Exercise:
-
- Engaging in moderate aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, or swimming can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Resistance training, when incorporated regularly, can assist in managing blood sugar levels.
Weight Management:
-
- Obesity can strain the pancreas. Losing weight, especially around the abdomen, can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of diabetes.
Stress Reduction:
-
- Chronic stress can affect insulin production. Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can significantly reduce stress and its impact on the pancreas.
Natural Supplements:
-
- Berberine: Often used in traditional medicine, berberine can enhance insulin sensitivity.
- Bitter Melon: This has been linked with increased insulin production in some studies.
Detoxification:
-
- Limiting or eliminating alcohol and tobacco can give your pancreas a much-needed break.
- Regular detox diets, when done responsibly, might also support pancreatic and overall health.
| STRATEGY | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| Dietary Changes | Low-Carb Diet: Reduces demand on pancreas for insulin production. Anti-inflammatory Foods: e.g., turmeric, berries, fatty fish. Stay Hydrated: Maintains cell health, including pancreatic cells. |
| Regular Exercise | Aerobic: e.g., walking, cycling, swimming for insulin sensitivity. Resistance Training: Helps manage blood sugar levels. |
| Weight Management | Obesity Reduction: Focus on abdominal area for insulin sensitivity. |
| Stress Reduction | Manage Chronic Stress: Techniques include meditation, deep breathing, and yoga. |
| Natural Supplements | Berberine: Enhances insulin sensitivity. Bitter Melon: Linked with increased insulin production. |
| Detoxification | Limit Alcohol and Tobacco: Provides pancreas relief. Detox Diets: Responsible detoxing may support overall health. |
| Medical Interventions | Medications/therapies might be required for insulin efficacy. |
Can the pancreas normally produce insulin again?
Recent research spearheaded by Professor Roy Taylor from Newcastle University has unearthed groundbreaking insights about Type 2 diabetes. Contrary to the earlier belief that insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas were irreparably damaged in those diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes, findings indicate that these cells can reactivate and regain functionality when an individual is in remission from the disease. These revelations came from the second-year findings of the DiRECT trial, funded by Diabetes UK. The study showed that achieving remission from Type 2 diabetes via a stringent low-calorie diet could sustain the remission for at least two years. Furthermore, people in remission exhibited a resurgence in their pancreas’s insulin-producing capability, restoring it to levels comparable to individuals without a Type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Notably, this resurgence in beta cell function was gradual, stabilizing in the second year and effectively maintaining blood glucose levels below the diabetic range. Professor Taylor emphasized the importance of sustained weight loss for maintaining this remission, pointing out that those who did not achieve remission in the DiRECT trial showed no beta cell recovery despite comparable weight loss. In a healthy individual, beta cells activate in response to rising blood glucose levels post-meal, releasing insulin to help the body utilize this glucose. This mechanism is disrupted in Type 2 diabetics, with the beta cell response believed to deteriorate progressively post-diagnosis. However, this study offers renewed hope, suggesting that with the right interventions, the body’s natural insulin-producing processes can indeed recover.
Reviving Pancreatic Cells
While stimulating the pancreas to produce more insulin is crucial, the revival of pancreatic cells, especially beta cells, is an evolving area of research. Some animal studies suggest that certain medications, fasting regimens, or stem cell therapies might hold the potential to regenerate these cells. However, more robust human trials are needed to ascertain the effectiveness of these methods.
Maintaining the health of the pancreas and stimulating it to produce insulin efficiently involves a combination of lifestyle choices, dietary habits, and sometimes medical interventions. Prioritizing your pancreatic health can go a long way in ensuring your body’s overall wellness and metabolic harmony. As always, consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your health regimen.
Fig: Revived pancreatic cells




