Introduction to Glycemic Responses and Prediabetes
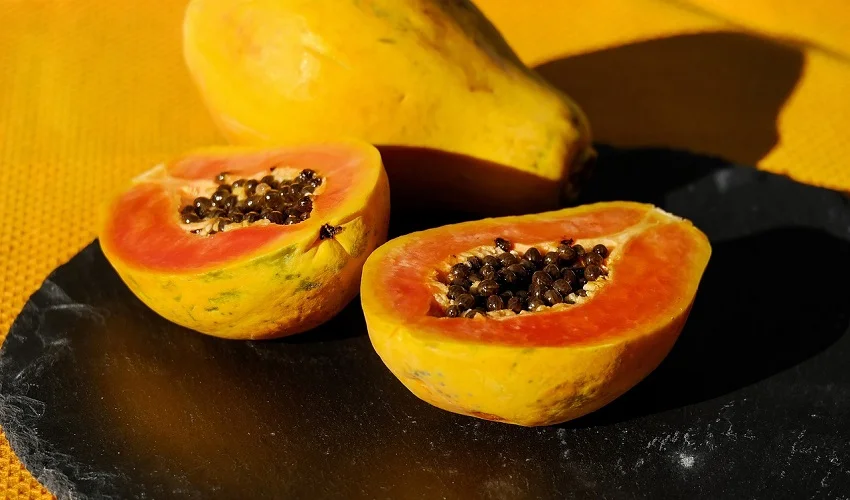
The consumption of fruits like papaya is often surrounded by cautionary advice for those with prediabetic conditions due to their natural sugar content. A recent observation has provided insights into how a moderate portion of papaya, approximately 150 grams, impacts blood sugar levels in a 42-year-old prediabetic individual.
Blood Sugar Levels and Papaya Consumption
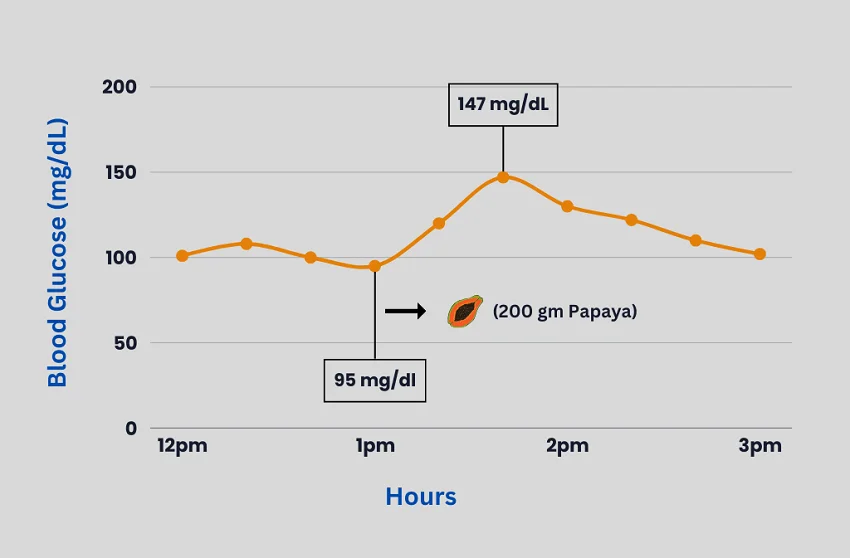
Upon the ingestion of papaya, the individual’s blood glucose levels were closely monitored. It was noted that there was a significant glycemic response: blood sugar levels spiked from 95 to 147 mg/dl within about 45 minutes post-consumption. This rapid increase brings to light the body’s glycemic reaction to the fruit’s carbohydrates.
The Nutritional Profile of Papaya
Papaya is a nutrient-dense fruit that offers a wealth of health benefits, including a rich supply of Vitamin C, antioxidants, and dietary fiber. However, the fruit’s carbohydrate content can lead to glucose level fluctuations, as evidenced by the data gathered from Care4Sugar’s continuous monitoring device-based programs. For a prediabetic, such spikes are critical markers, highlighting the need for careful dietary planning.
Analyzing the Glucose Spike
The graph provided below illustrates the pointed increase in glucose levels, marked by a noticeable spike shortly after the papaya intake. This visual representation underscores the immediate impact of the fruit on blood sugar levels, a concern for those managing prediabetic conditions. It is essential for individuals with blood sugar sensitivities to consider the timing, portion size, and ripeness of fruits like papaya in their diet.
Implications for Dietary Planning
The data derived from the observed glycemic response to papaya consumption is a call to action for healthcare professionals, underscoring the critical need for personalized dietary planning. This individualized approach is paramount, particularly for those navigating the complexities of prediabetes.
Fruits, with their array of essential nutrients, form a cornerstone of a well-rounded diet. However, as demonstrated, the natural sugars present in fruits like papaya can lead to significant blood sugar fluctuations in individuals with prediabetes. Healthcare providers must, therefore, consider the unique glycemic impact on each individual when making dietary recommendations. This tailored strategy should take into account the person’s blood sugar patterns, lifestyle, and overall health goals.
Education plays a crucial role in empowering patients with prediabetes to make informed decisions about their diet. It is vital to provide clear guidelines on which fruits, portions, and frequencies are optimal for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. In addition, teaching patients how to monitor their own blood sugar responses to different foods can help them better understand and manage their condition.
Nutritional counseling should be integrated into the patient care plan for those with prediabetes. Registered dietitians and nutritionists can work closely with patients to develop eating plans that not only address the management of blood glucose levels but also support overall health and wellness.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Prediabetes management is not a static process; it requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. As patients’ health situations evolve, so too should their eating plans. Regular check-ins with healthcare professionals can ensure that dietary recommendations remain effective and responsive to the patients’ needs.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, while the moderate consumption of papaya offers nutritional benefits, it is imperative that prediabetic individuals consume it with caution. Monitoring blood sugar levels in response to dietary intake can provide valuable insights, enabling adjustments for better health outcomes. This case serves as a reminder of the delicate balance that must be maintained in the dietary management of prediabetes.




