Living with diabetes can bring about various complications, and one of the most common and concerning is diabetic neuropathy. In the world of medical coding and diagnosis, the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) plays a crucial role in accurately identifying and documenting conditions. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of Diabetic Neuropathy ICD-10, shedding light on its significance, codes, and implications.
What is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic Neuropathy is a nerve disorder that occurs as a result of prolonged high blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. It can affect various nerves throughout the body, leading to a range of symptoms that may impact sensory, motor, and autonomic functions.
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy involves damage to the peripheral nerves, causing symptoms like numbness, tingling, and pain in the extremities. This type of neuropathy often affects the feet and legs.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic Neuropathy affects the nerves controlling involuntary bodily functions such as digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure. Symptoms may include gastrointestinal issues, dizziness, and irregular heartbeat.
Proximal Neuropathy
Proximal Neuropathy, also known as diabetic amyotrophy, causes pain and muscle weakness in the hips, thighs, and legs. It typically affects one side of the body.
Focal Neuropathy
Focal Neuropathy leads to sudden weakness or pain in specific nerves or groups of nerves. It can impact the eyes (cranial neuropathy), torso, or legs, and often occurs abruptly.
Distribution of Diabetic Neuropathy Types:
| Neuropathy Type | Percentage of Diabetic Neuropathy Cases |
|---|---|
| Diabetic Polyneuropathy (G63.2) | 60% |
| Diabetic Mononeuropathy (G73.5) | 25% |
| Other Neuropathies | 15% |
ICD-10 Codes for Diabetic Neuropathy
In medical coding, the ICD-10 system is used to classify diseases and conditions. Here are the primary ICD-10 codes associated with Diabetic Neuropathy:
- E11.40 – Type 2 Diabetes with Diabetic Neuropathy
- E10.40 – Type 1 Diabetes with Diabetic Neuropathy
These codes help healthcare professionals accurately document and bill for cases of Diabetic Neuropathy in patients with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
The symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy can vary based on the type and extent of nerve damage. Common symptoms include:
- Numbness and Tingling: Patients may experience a “pins and needles” sensation, especially in their extremities.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in muscles, particularly in the legs, can make mobility challenging.
- Digestive Issues: Autonomic Neuropathy may lead to problems like nausea, vomiting, constipation, or diarrhea.
- Cardiovascular Symptoms: Autonomic Neuropathy can also affect heart rate and blood pressure regulation, potentially causing dizziness and fainting.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosis of Diabetic Neuropathy involves a combination of clinical evaluation and specialized tests:
- Clinical Examination: A thorough physical examination can reveal sensory changes, reflex abnormalities, and muscle weakness.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests assess the speed and strength of electrical signals in nerves, aiding in diagnosing nerve damage.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles, helping to identify nerve dysfunction.
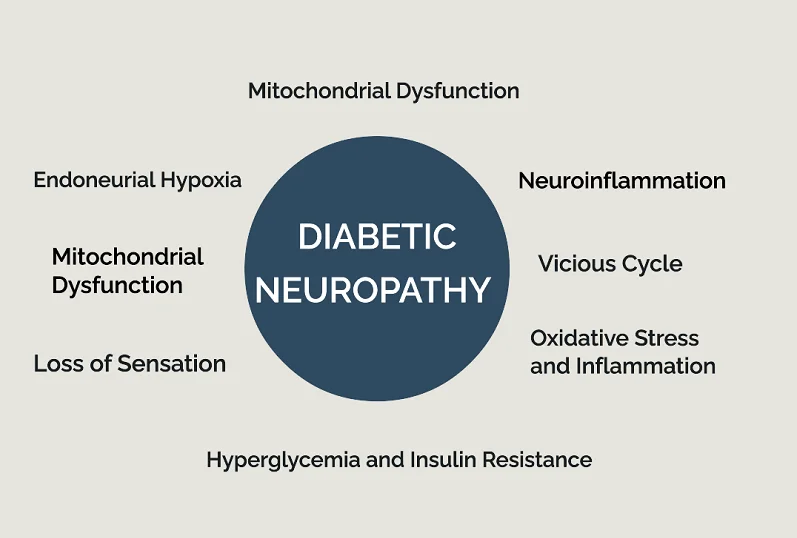
Chain of Diabetic Neuropathy
Collaborative Care Approach
Managing Diabetic Neuropathy often requires a collaborative effort from various medical professionals:
- Endocrinologist Consultation: Managing blood sugar levels is crucial, making an endocrinologist a key figure in the patient’s care team.
- Neurologist Involvement: Neurologists specialize in diagnosing and treating nervous system disorders, providing expertise in managing neuropathy symptoms.
- Pain Management Specialist: For patients experiencing chronic pain, a pain management specialist can recommend appropriate interventions.
Lifestyle Modifications
Several lifestyle modifications can positively impact Diabetic Neuropathy:
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining stable blood sugar levels can slow the progression of nerve damage.
- Foot Care Regimen: Proper foot care reduces the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
- Diet and Exercise: A balanced diet and regular exercise contribute to overall well-being and blood sugar control.
Medication and Therapies
Various medications and therapies can alleviate Diabetic Neuropathy symptoms:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers can help manage neuropathic pain.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressant medications also provide pain relief for neuropathy.
- Topical Creams: Topical treatments containing capsaicin or lidocaine can ease localized discomfort.
Treatment and Management:
| Treatment | Percentage of Diabetic Neuropathy Cases |
|---|---|
| Medications | 70% of individuals with Diabetic Neuropathy |
| Physical Therapy | 40% of individuals with Diabetic Neuropathy |
Prevention Strategies
Preventing Diabetic Neuropathy involves proactive measures:
- Glycemic Control: Maintaining target blood sugar levels significantly reduces the risk of nerve damage.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups and screenings allow for early detection and intervention.
- Foot Care Awareness: Proper foot hygiene and inspections can prevent complications.
Living With Diabetic Neuropathy
Living with Diabetic Neuropathy can present various challenges, but with proper management and lifestyle adjustments, it’s possible to improve your quality of life and minimize the impact of the condition. Here are some important considerations for those living with Diabetic Neuropathy:
- Diabetes Management: Maintaining good blood sugar control is essential. Work closely with your healthcare team to manage your diabetes through proper medication, diet, exercise, and regular monitoring.
- Pain Management: If you experience pain, work with your healthcare provider to develop a pain management plan. This could involve medications, physical therapy, acupuncture, or other pain-relief techniques.
- Blood Pressure Control: Maintain healthy blood pressure levels to minimize the risk of cardiovascular complications that can exacerbate neuropathy.
- Healthy Diet: Follow a balanced diet that supports your diabetes management. Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. This can help control blood sugar levels and support nerve health.