Living with diabetes requires constant monitoring of blood glucose levels to manage the condition effectively. Traditional glucose monitoring methods, such as fingerstick blood tests, have been the norm for many years. However, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems have emerged as a game-changing technology, providing numerous benefits to individuals with diabetes. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of CGM systems, their benefits, and their usage, offering valuable information to diabetic patients and caregivers.
Understanding Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems
What are CGM Systems?
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems are devices designed to measure glucose levels continuously throughout the day and night. Unlike traditional fingerstick tests, CGM systems offer real-time data, providing a comprehensive picture of glucose fluctuations and trends over time.
How do CGM Systems Work?
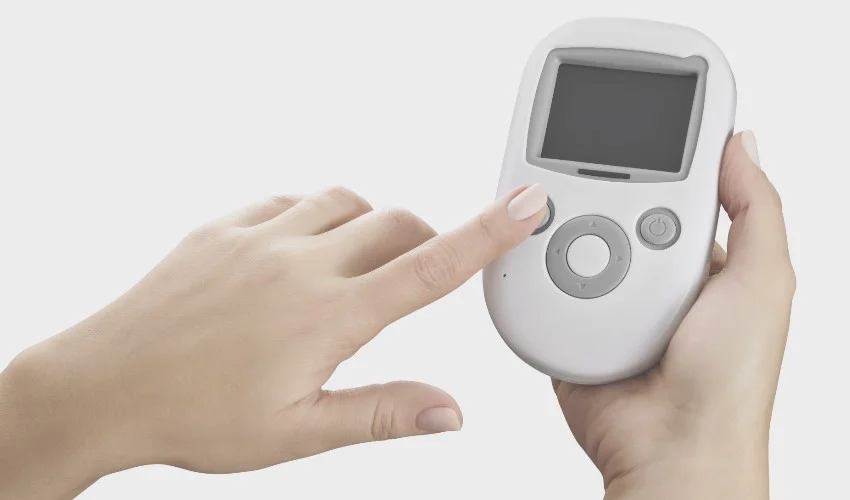
CGM systems consist of three main components: a glucose sensor, a transmitter, and a receiver or smartphone app. The glucose sensor is typically inserted under the skin, often in the abdomen, where it measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor sends this data to the transmitter, which wirelessly transmits the information to the receiver or app. Users can view their glucose levels and trends on the receiver or app, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding diabetes management.
Benefits of CGM Systems
Real-time Glucose Data
One of the key advantages of CGM systems is the provision of real-time glucose data. Instead of relying on sporadic fingerstick tests, users can access continuous updates on their glucose levels. This information helps identify patterns and trends that may be missed with traditional testing, allowing for more precise and timely adjustments to diabetes management strategies.
Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia Alerts
CGM systems are equipped with alarms and alerts that notify users of potential hypoglycemic (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemic (high blood sugar) episodes. These alerts are especially valuable for individuals who may not experience symptoms or have difficulty recognizing them. Early detection and intervention can prevent severe fluctuations in blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications.
Reduced Need for Fingerstick Tests
While fingerstick tests remain necessary for calibration and confirmation, CGM systems significantly reduce the number of daily fingersticks required for glucose monitoring. This reduction in fingerstick tests improves convenience, reduces discomfort, and minimizes the disruption of daily activities, enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Improved Time in Range
Time in Range (TIR) refers to the percentage of time spent within target blood glucose ranges. CGM systems contribute to improving TIR by providing a more comprehensive and continuous view of glucose fluctuations. With accurate and timely data, users can make informed decisions regarding medication, diet, and physical activity to keep their blood glucose within the desired range, ultimately reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Trend Analysis and Predictive Insights
CGM systems offer valuable trend analysis and predictive insights by displaying glucose trends over time. Users can identify patterns such as post-meal spikes, nocturnal hypoglycemia, or dawn phenomenon, helping them make adjustments to their treatment plans and lifestyle choices accordingly. These insights empower individuals to take proactive measures to manage their diabetes effectively.
CGM System Usage and Considerations
Choosing a CGM System
When selecting a CGM system, it is essential to consider factors such as accuracy, reliability, ease of use, and compatibility with other devices. Consulting with healthcare professionals and comparing different CGM systems based on features, user reviews, and cost can assist in making an informed decision.
Insertion and Wear
Inserting the glucose sensor is a critical aspect of using a CGM system. Proper insertion techniques, following manufacturer guidelines, can ensure accurate readings and reduce discomfort. The duration of sensor wear varies depending on the system, ranging from a few days to several weeks. Users should carefully follow instructions regarding sensor replacement to maintain accurate and reliable readings.
Calibration and Accuracy
CGM systems require periodic calibration with fingerstick tests to ensure accuracy. Following the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration and recognizing the impact of factors like medications, exercise, and hydration on glucose readings is vital. Users should also be aware of the possibility of sensor errors and take appropriate actions, such as double-checking readings with fingerstick tests when necessary.
Table: An overview of different CGM systems available in the market, along with their key features:
| CGM System | Sensor Wear Duration | Calibration Requirement | Compatibility with Smartphones | Hypoglycemia Alerts | Hyperglycemia Alerts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System A | 7-14 days | Twice daily | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| System B | 10-14 days | Once daily | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| System C | 14-21 days | No calibration | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| System D | 7 days | Twice daily | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| System E | 14 days | Once daily | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time glucose data, reducing the need for fingerstick tests, and offering valuable insights into glucose trends. The benefits of CGM systems include improved time in range, hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia alerts, and the ability to make proactive adjustments to diabetes management. Choosing the right CGM system and following proper usage guidelines are crucial for maximizing the benefits and accuracy of these devices.
As technology continues to advance, CGM systems are expected to become even more sophisticated, offering enhanced features and improved user experiences. By embracing CGM technology, individuals with diabetes can gain greater control over their condition, leading to improved health outcomes and an enhanced quality of life.