What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or does not effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and allows cells to absorb glucose for energy. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity. Both types of diabetes require careful management to prevent complications and maintain blood sugar levels within a target range.
Understanding blood sugar levels
Blood sugar levels refer to the amount of glucose present in the bloodstream. Understanding blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes as it helps them manage their condition effectively. High blood sugar levels, also known as hyperglycemia, can lead to various complications such as nerve damage, heart disease, and kidney problems. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels, known as hypoglycemia, can cause symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and making appropriate dietary and lifestyle adjustments are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
The role of diet in managing diabetes
Diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. It is important for individuals with diabetes to carefully consider their food choices to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Carrots, in particular, can be a beneficial addition to a diabetic diet. Although carrots are relatively high in natural sugars, they also contain essential nutrients such as fiber, vitamin A, and potassium. These nutrients can help regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and support overall health. However, it is important to consume carrots in moderation and incorporate them as part of a balanced meal plan that includes a variety of other vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
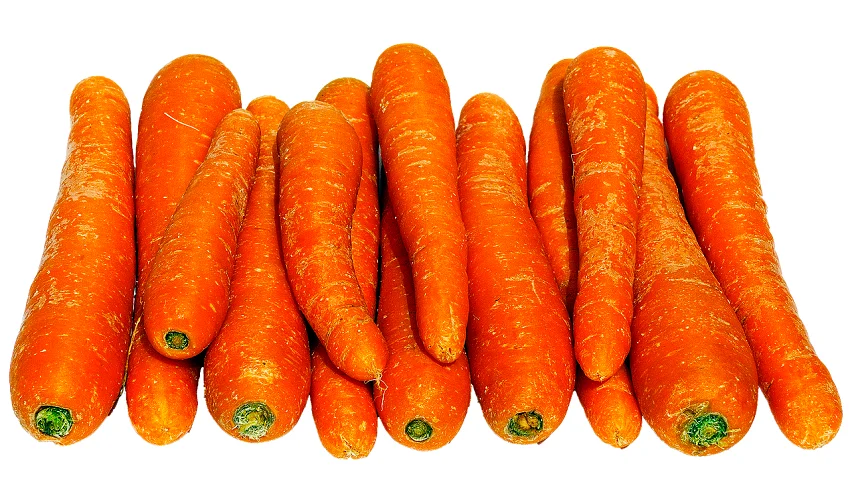
Carrots and Diabetes
Nutritional profile of carrots
Carrots have a rich nutritional profile that makes them a great choice for diabetics. They are low in calories and carbohydrates, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. Carrots are also a good source of fiber, which aids in digestion and helps control blood sugar spikes. Additionally, they are packed with vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, vitamin C, and potassium, which are important for overall health and well-being. Incorporating carrots into a balanced diet can provide diabetics with essential nutrients while keeping their blood sugar in check.
Effect of carrots on blood sugar levels
Carrots have a low glycemic index, which means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. This makes them a suitable choice for individuals with diabetes. Carrots are also rich in fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Additionally, carrots contain antioxidants, such as beta-carotene, that have been shown to reduce the risk of developing diabetes complications. However, it is important to consume carrots in moderation as part of a balanced diet to ensure overall blood sugar control.
Benefits of carrots for diabetics
Carrots are a highly nutritious vegetable that can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes. They are low in calories and high in fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels. Carrots also contain antioxidants, such as beta-carotene, which can help reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Additionally, carrots are a good source of vitamins A and C, which can support overall immune function. Including carrots in a balanced diet can be a healthy choice for individuals with diabetes.
Carrots and Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance and its impact on diabetes
Insulin resistance is a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and eventually the development of type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance is often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars. It is important for individuals with diabetes to manage their insulin resistance through lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and medication if necessary. By addressing insulin resistance, individuals with diabetes can better control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Can carrots help improve insulin sensitivity?
They are low in calories and have a low glycemic index, which means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Additionally, carrots are rich in fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. The high fiber content in carrots slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar. Furthermore, carrots are a good source of antioxidants, including beta-carotene, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Incorporating carrots into a balanced diet can be a healthy choice for individuals with diabetes.
Research on carrots and insulin resistance
Carrots have been the subject of research when it comes to their effect on insulin resistance. Several studies have shown that carrots may have a positive impact on insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for individuals with diabetes. One study found that the antioxidants in carrots can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are associated with insulin resistance. Another study suggested that the high fiber content in carrots may contribute to improved blood sugar control. However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between carrots and insulin resistance. Overall, incorporating carrots into a balanced diet may be a good choice for individuals with diabetes, but it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice.
Carrots and Glycemic Index
Understanding the glycemic index
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Understanding the glycemic index can be particularly important for diabetics, as it helps them make informed choices about the foods they consume. Carrots have a low glycemic index, which means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. This makes them a good choice for diabetics as part of a balanced diet. However, it is important to note that portion control is still necessary, as consuming large quantities of any food, including carrots, can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Therefore, diabetics should consult with their healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate portion sizes and frequency of carrot consumption based on their individual needs and blood sugar management goals.
Glycemic index of carrots
Carrots have a low glycemic index, making them a suitable choice for diabetics. The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index, such as carrots, are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual and steady increase in blood sugar. This can help prevent spikes in blood sugar levels, which is particularly important for individuals with diabetes. Additionally, carrots are rich in fiber, which further helps regulate blood sugar levels and promote overall health. Including carrots in a balanced diet can be beneficial for diabetics in managing their blood sugar levels.
How carrots affect blood sugar levels
Carrots can have a positive effect on blood sugar levels for diabetics. Although carrots contain natural sugars, they also have a low glycemic index, which means they are digested and absorbed slowly. This slow digestion helps prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, carrots are high in fiber, which further aids in regulating blood sugar levels. The combination of low glycemic index and high fiber content makes carrots a healthy choice for diabetics looking to manage their blood sugar levels.
Incorporating Carrots into a Diabetic Diet
Portion control and moderation
Portion control and moderation are important factors to consider when including carrots in a diabetic diet. While carrots are generally low in carbohydrates and have a low glycemic index, it is still essential to monitor portion sizes to maintain stable blood sugar levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends consuming no more than 1/2 cup of cooked carrots or 1 cup of raw carrots as part of a balanced meal. Additionally, it is important to incorporate carrots into a well-rounded meal plan that includes a variety of other vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. By practicing portion control and moderation, individuals with diabetes can enjoy the nutritional benefits of carrots while managing their blood sugar levels effectively.
Cooking methods for carrots
Carrots can be cooked in various ways to enhance their flavor and nutritional value. One popular method is roasting, which involves coating the carrots in olive oil, sprinkling them with salt and pepper, and baking them in the oven until they are tender and caramelized. Another option is steaming, which helps retain the carrots’ natural sweetness and nutrients. Boiling is another simple method, where the carrots are cooked in boiling water until they are soft. Additionally, carrots can be stir-fried with other vegetables to create a delicious and colorful side dish. Whichever cooking method you choose, carrots can be a healthy and tasty addition to a diabetic-friendly diet.
Other vegetables to include with carrots
Carrots are not the only vegetable that can benefit diabetics. There are several other vegetables that can be included in the diet along with carrots. Some of these vegetables include leafy greens like spinach and kale, which are rich in fiber and low in carbohydrates. Broccoli is another great option, as it is high in fiber and contains a compound called sulforaphane, which may help regulate blood sugar levels. Other vegetables to consider include bell peppers, cucumbers, and zucchini, all of which are low in carbohydrates and provide important vitamins and minerals. By incorporating a variety of vegetables into the diet, diabetics can enjoy a wide range of flavors and nutrients while keeping their blood sugar levels in check.
Summary of the benefits of carrots for diabetics
They are low in calories and have a low glycemic index, which means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Carrots are also rich in fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Additionally, they contain antioxidants and vitamins that support overall health and may reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Including carrots in a balanced diet can be a healthy choice for individuals with diabetes.
Importance of a balanced diet
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining good health and managing diabetes. It involves consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods in appropriate portions to provide the body with the necessary energy and nutrients. Carrots, in particular, can be a beneficial addition to a balanced diet for diabetics. They are low in calories and have a low glycemic index, meaning they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Additionally, carrots are rich in fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and improve digestion. They also contain antioxidants and vitamins that support overall health. However, it is important to consume carrots in moderation and as part of a well-rounded meal plan, as excessive intake may lead to an increase in blood sugar levels. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help determine the appropriate amount of carrots to include in a diabetic diet.
Consulting a healthcare professional
Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for individuals with diabetes, especially when it comes to making dietary choices. While carrots are generally considered a healthy vegetable, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before including them in your diet. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific health needs and help you determine whether carrots are suitable for your diabetes management plan. Your healthcare professional can also help you understand the impact of carrots on blood sugar levels and recommend appropriate portion sizes. Remember, each person’s diabetes management plan is unique, so it’s essential to seek professional advice before making any changes to your diet.