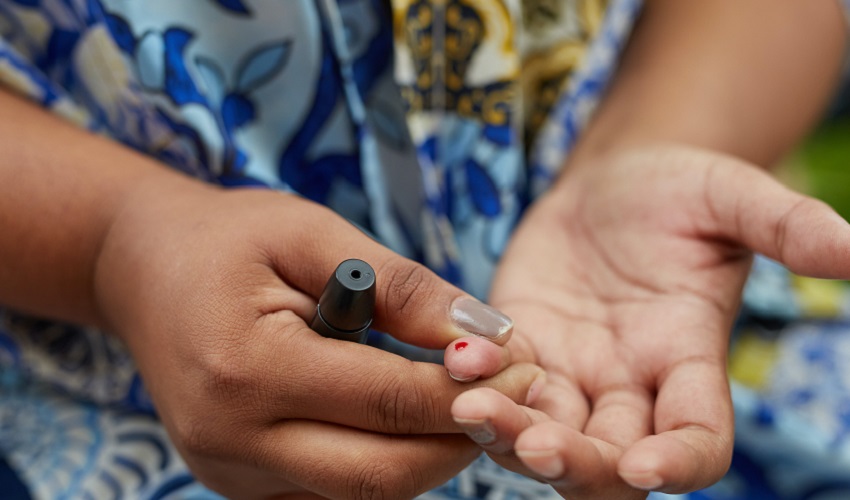
Introduction to glucose administration
Glucose administration plays a crucial role in the management of patients, particularly those who are unable to maintain adequate blood sugar levels on their own. It serves as a vital source of energy for the body and is commonly used in medical settings to provide support to patients with various conditions. The introduction of glucose administration involves understanding its importance and how it can positively impact patient outcomes. By ensuring a steady supply of glucose, healthcare professionals can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of glucose administration and discuss how long a patient may need to be given glucose depending on their individual circumstances.
Importance of glucose for patients
Glucose plays a crucial role in the management and treatment of patients. It serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, providing fuel for various physiological processes. For patients, especially those who are critically ill or have certain medical conditions, glucose is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and preventing complications. It helps to replenish glycogen stores, supports brain function, and promotes tissue repair and healing. Additionally, glucose administration can be vital during surgeries, trauma, or periods of fasting when the body’s glucose reserves may be depleted. Overall, the importance of glucose for patients cannot be overstated, as it contributes significantly to their overall well-being and recovery.
Different methods of glucose administration
Different methods of glucose administration include oral intake, intravenous infusion, and subcutaneous injection. Oral intake is the most common method, where glucose is consumed through food and drinks. Intravenous infusion is used when a patient is unable to consume food orally or requires immediate glucose delivery. Subcutaneous injection involves injecting glucose directly into the fatty tissue under the skin. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of administration depends on the patient’s condition and medical requirements.
Glucose Administration in Emergency Situations
Glucose administration in diabetic emergencies
Glucose administration plays a crucial role in managing diabetic emergencies. When a patient experiences an episode of hypoglycemia or low blood sugar, the immediate administration of glucose can be life-saving. Glucose provides the necessary fuel for the body’s cells, especially the brain, which heavily relies on glucose for energy. In diabetic emergencies such as diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, glucose administration is essential in correcting the underlying metabolic imbalance. It helps restore blood sugar levels to a safe range and prevents further complications. Additionally, glucose administration should be closely monitored to avoid excessive fluctuations in blood sugar levels and ensure optimal glycemic control. Overall, the timely and appropriate administration of glucose is vital in managing diabetic emergencies and promoting the well-being of patients.
Glucose administration in hypoglycemic patients
Glucose administration in hypoglycemic patients plays a crucial role in restoring blood sugar levels to normal. When a patient experiences low blood sugar levels, providing them with glucose is essential to prevent further complications. Glucose acts as a source of immediate energy, quickly raising blood sugar levels and alleviating symptoms of hypoglycemia. It can be administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the condition. In cases of severe hypoglycemia, intravenous glucose administration is preferred for rapid absorption. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and appropriate dosage adjustments are necessary to ensure effective glucose administration and maintain optimal glucose levels in hypoglycemic patients.
Glucose administration in unconscious patients
Glucose administration in unconscious patients plays a crucial role in providing the necessary energy for their body functions. When a patient is unconscious, their ability to regulate blood sugar levels is compromised, making it essential to provide external glucose support. This is typically done through intravenous administration, ensuring a rapid and direct supply of glucose to the bloodstream. By maintaining adequate glucose levels, healthcare professionals can help prevent complications and promote recovery in unconscious patients.
Glucose Administration during Surgery
Pre-operative glucose administration
Pre-operative glucose administration is an essential aspect of patient care before undergoing surgery. The administration of glucose helps to maintain the patient’s blood sugar levels within a normal range, ensuring optimal physiological functioning. This is particularly important as surgery can induce stress, which may lead to fluctuations in blood glucose levels. By providing glucose pre-operatively, healthcare professionals can help to prevent hypoglycemia, which can have detrimental effects on the patient’s overall health and recovery. Additionally, glucose administration can also support the patient’s energy levels and enhance their ability to tolerate the surgical procedure. Overall, pre-operative glucose administration plays a crucial role in ensuring the patient’s well-being and promoting successful surgical outcomes.
Intra-operative glucose administration
Intra-operative glucose administration refers to the administration of glucose to a patient during a surgical procedure. It is an important aspect of patient care as it helps maintain blood glucose levels within a normal range. During surgery, the body’s metabolism and energy requirements may increase, leading to a decrease in blood glucose levels. In order to prevent hypoglycemia and ensure optimal patient outcomes, healthcare providers may administer glucose intravenously or through other routes. The dosage and duration of glucose administration during surgery depend on various factors such as the patient’s preoperative glucose levels, the duration of the procedure, and the patient’s overall health status. Continuous monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial during intra-operative glucose administration to ensure the patient’s safety and well-being.
Post-operative glucose administration
Post-operative glucose administration plays a crucial role in the recovery process of a patient. After a surgical procedure, the body’s glucose levels can be significantly affected, leading to a state of hypoglycemia. To prevent this, healthcare professionals administer glucose to patients to maintain their blood sugar levels within a normal range. This helps provide the necessary energy for the body to heal and recover. The duration of post-operative glucose administration varies depending on the individual patient and the specific surgical procedure. It is typically continued until the patient’s glucose levels stabilize and they are able to maintain normal blood sugar levels independently. Close monitoring and regular assessments are essential to determine the appropriate duration of glucose administration for each patient.
Glucose Administration in Critical Care
Glucose administration in ICU patients
Glucose administration in ICU patients plays a crucial role in maintaining their energy levels and promoting recovery. In the intensive care unit (ICU), patients often experience a high metabolic demand due to their critical condition. Therefore, providing glucose intravenously is essential to meet their nutritional needs and prevent hypoglycemia. Additionally, glucose administration helps support vital organ function and aids in the healing process. It is important for healthcare professionals to closely monitor glucose levels and adjust the administration rate accordingly to ensure optimal patient outcomes. Overall, glucose administration in ICU patients is a vital component of their care and contributes to their overall well-being and recovery.
Monitoring glucose levels in critically ill patients
Monitoring glucose levels in critically ill patients is crucial to ensure optimal care and management. In the intensive care unit, continuous monitoring of glucose levels allows healthcare providers to assess the patient’s response to treatment and make necessary adjustments. High glucose levels can indicate stress, infection, or other underlying medical conditions, while low glucose levels can lead to complications such as hypoglycemia. Regular monitoring helps in maintaining glucose levels within the target range, promoting better outcomes and reducing the risk of adverse events. It also provides valuable information for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding insulin therapy and other interventions. Overall, monitoring glucose levels in critically ill patients is an essential component of their care, ensuring their well-being and facilitating their recovery.
Optimal glucose range for critically ill patients
The optimal glucose range for critically ill patients is a topic of ongoing debate and research. Maintaining blood glucose levels within a specific range is crucial for the overall well-being and recovery of these patients. While some studies suggest that tight glycemic control with lower glucose levels may improve outcomes, others argue that a more liberal approach with slightly higher glucose levels is safer. Factors such as the severity of illness, individual patient characteristics, and the presence of comorbidities need to be taken into consideration when determining the optimal glucose range for each patient. Close monitoring and regular adjustments of glucose levels are necessary to ensure that patients receive the appropriate amount of glucose to support their energy needs without causing harm. The goal is to strike a balance between preventing hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, as both extremes can have detrimental effects on the patient’s health. Further research is needed to provide more definitive guidelines on the optimal glucose range for critically ill patients.
Glucose Administration in Chronic Illness
Glucose administration in cancer patients
Glucose administration in cancer patients plays a crucial role in their overall treatment and management. Cancer cells have a higher demand for glucose compared to normal cells, as they rely heavily on this energy source for their rapid growth and proliferation. Therefore, providing glucose to cancer patients helps meet their increased energy needs and supports their immune system function. Additionally, glucose administration can help alleviate the side effects of cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. However, it is important to closely monitor glucose levels in cancer patients to prevent complications, as excessive glucose administration can lead to hyperglycemia. Overall, the judicious administration of glucose in cancer patients is an essential component of their comprehensive care plan.
Glucose administration in HIV/AIDS patients
Glucose administration plays a crucial role in the management of HIV/AIDS patients. Due to the compromised immune system and increased metabolic demands, individuals living with HIV/AIDS often experience significant weight loss and malnutrition. Glucose is essential for providing energy and supporting vital bodily functions. By administering glucose, healthcare providers can help stabilize blood sugar levels, improve overall nutrition, and enhance the immune response in HIV/AIDS patients. It is important to monitor glucose levels closely and adjust the administration accordingly to ensure optimal health outcomes for these individuals.
Glucose administration in renal failure patients
Glucose administration in renal failure patients is a crucial aspect of their overall management. Renal failure can significantly affect the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to complications such as hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Therefore, providing glucose to these patients becomes essential to maintain stable blood sugar levels. However, the administration of glucose in renal failure patients requires careful monitoring and individualized approach as excessive glucose intake can further burden the already compromised kidneys. It is important to consider the patient’s renal function, nutritional status, and concurrent medications while determining the appropriate dosage and frequency of glucose administration. Close monitoring of blood glucose levels and regular assessment of renal function are necessary to prevent any adverse effects and optimize the patient’s overall well-being.
Summary of glucose administration
Glucose administration is an essential aspect of patient care, particularly in cases where there is a need to maintain adequate blood sugar levels. The summary of glucose administration highlights the duration for which a patient should be given glucose. This is determined by various factors, including the underlying medical condition, the severity of the patient’s symptoms, and the response to treatment. It is crucial to closely monitor the patient’s blood glucose levels and adjust the administration accordingly. The goal is to ensure that the patient receives the necessary glucose support for their overall well-being and recovery. By carefully assessing the patient’s needs and providing appropriate glucose administration, healthcare professionals can contribute to the patient’s optimal health outcomes.
Importance of individualized glucose management
Individualized glucose management is of paramount importance in patient care. Each patient has unique needs and requirements when it comes to glucose management. It is crucial to tailor the treatment plan according to the patient’s specific condition, such as their medical history, current health status, and any underlying conditions. By providing individualized glucose management, healthcare professionals can optimize patient outcomes and ensure the best possible care. This approach allows for personalized monitoring, adjustment of glucose levels, and prevention of complications related to glucose imbalance. Ultimately, individualized glucose management plays a crucial role in promoting patient well-being and overall health.
Future directions in glucose administration
In the future, the administration of glucose to patients may undergo significant advancements. One potential direction is the development of more targeted glucose delivery systems, which can ensure precise and controlled glucose levels in the body. This could help in preventing both hypo- and hyperglycemia, leading to better management of glucose levels in patients. Additionally, the use of continuous glucose monitoring devices may become more widespread, allowing healthcare providers to closely monitor glucose levels in real-time and make timely adjustments in treatment plans. Furthermore, research in the field of glucose metabolism and its impact on various diseases may uncover new therapeutic approaches, leading to improved patient outcomes. Overall, the future of glucose administration holds promise for more personalized and effective management of glucose levels in patients.